The Philippines is an archipelago comprised of more than 7,000
islands lying about 500 miles southeast of mainland Asia. Its closest
nation neighbors are Malaysia and Indonesia to its south.
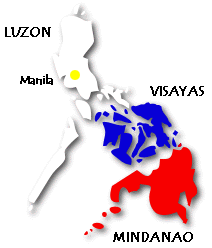 The island group consists
of three geographical and cultural main island groups of Luzon,
Visayas, and Mindanao. Of the 7,000 islands only 360 have areas of
one square mile or bigger and only about 2,700 are named. Many are
uninhabited and uncharted. Luzon, the largest island, has a land area
of 40,420 square miles. The second largest island, Mindanao, has a
land area of 36,537 square miles. The total land area of the
Philippines is 115,830. The island group consists
of three geographical and cultural main island groups of Luzon,
Visayas, and Mindanao. Of the 7,000 islands only 360 have areas of
one square mile or bigger and only about 2,700 are named. Many are
uninhabited and uncharted. Luzon, the largest island, has a land area
of 40,420 square miles. The second largest island, Mindanao, has a
land area of 36,537 square miles. The total land area of the
Philippines is 115,830.
The islands are primarily composed of coral and volcanic rock and
feature mountainous country, interconnected volcanoes, lakes and
rivers. Scientists say that the Philippine volcanoes are part of
the Pacific "Ring of Fire" that includes the islands of Hawaii and
the San Andreas Fault along the Pacific coasts of the American
continent. Mount Pinatubo is known for its violent eruption in 1991.
The most prominent mountain chain is the Cordillera Central running
the length of Luzon Island which is composed of several large parallel
mountain ranges. Run-offs from the constant forest rain running down
the large mountain ranges feed several rivers and lakes that are
important to the agricultural, fishery and commercial livelihood of
Filipinos. |